The Role of Radiographer in Modern Healthcare
- Radiography
- April 24, 2024
- 2.2k views
- 4 min read
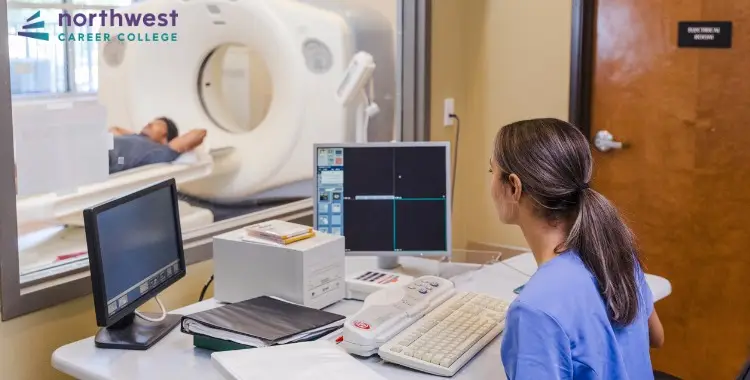
The field of radiography is undergoing significant changes, particularly in terms of the new generation of radiographers. More than ever, people pursuing a career in the radiography field are intentional about their long-term professional trajectory and do not settle for any position that comes their way.
So, what exactly does a radiographer do, and how do they fit into modern healthcare? If you’ve been asking yourself this question, you’ve come to the right place.
Table of Contents
The Basics of Radiography
Capturing Images
Radiographers leverage cutting-edge technology to capture high-quality images of the human body. They contribute to the modern healthcare industry by specializing in the use of advanced imaging modalities such as X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) scans. The images they capture are necessary for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
The breakthroughs in modern imaging technologies have brought unsurpassed detail and precision to the radiography field. These technological advances allow radiographers to capture internal structural images with incredible clarity and resolution so that radiologists and other healthcare providers can make more informed recommendations to their patients.
Image Analysis and Processing
After exposing the images, radiographers use special computer programs to enhance them. Adjusting brightness and contrast ensures that images come out clearly. These image enhancements help radiologists and other healthcare providers better understand what they see in the images and make proper patient care decisions.
Documentation and Reporting
A radiographer is a good record keeper. They record details about patient interactions, such as their patients’ names, the imaging procedures they had done, and any noteworthy clinical observations made during the procedures. Some of the technical information produced by the imaging procedures includes the settings used on the machine. But most importantly, images are noted down, and the recorded values are measured from these images. The information, measurements, and other details are then stored in medical records or reports that are highly secured, maintaining privacy and accuracy for each patient.
Collaboration with Healthcare Teams
Team Player
Radiographers are not independent practitioners in the healthcare system; however, they are among its fundamental blocks. They work under the health sector staff in medical services, including physicians, nurses, and others, all for the good of holistic patient care.
Diagnostic Support
Radiographers are not mere button-pushers but resources that doctors rely upon when interpreting the imaging results. Their clinical notes help the radiologist understand the patient’s history, positioning techniques, and any difficulties observed while taking the image.
Continuous Learning
Radiographers are lifelong learners and incorporate new and updated skills and knowledge towards technological development and medical updates. They participate in continuing education programs and go the extra mile to keep abreast with the latest developments in their field.
Advancements in Radiography Technology
Advancements in radiography technology have revolutionized the field, as they have in all industries. The trend is best epitomized by the transition from traditional film-based techniques to digital imaging systems.
Other advancements include the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI), which promises to revolutionize radiography practice with AI image analysis and interpretation tools. In that regard, AI algorithms help detect abnormalities and can significantly advance the level of diagnostic precision of radiologists.
Telemedicine is increasingly participating in the evolution and expansion of radiography services offered in teleradiology. It allows the completion of an imaging assessment but at a distance. Radiography technologists participate in teleradiology by capturing images and sending them to teleradiologists for remote consultations, improving efficiency while ensuring patient confidentiality. This practice further strengthens the argument that radiography is still evolving and has a profound impact on the delivery of health care.
Conclusion
The role of the radiographer in modern healthcare cannot be understated. From clear image capturing to collaborative work in healthcare and leadership in technological improvement, radiographers impact patients’ lives and serve on the frontline of medical imaging.




